Last Updated: January 7, 2026, 4 pm UTC
In recent years, the pharmaceutical landscape for rare diseases has witnessed a remarkable evolution. Rare diseases, often referred to as orphan diseases, affect small patient populations, yet collectively they impact more than 300 million people worldwidei and account for a significant portion of the global clinical development pipeline.
This blog delves into the rise of rare disease drug approvals and the critical importance of regulatory guidance in shaping the future of rare disease drug development.
The surge in rare disease drug approvals
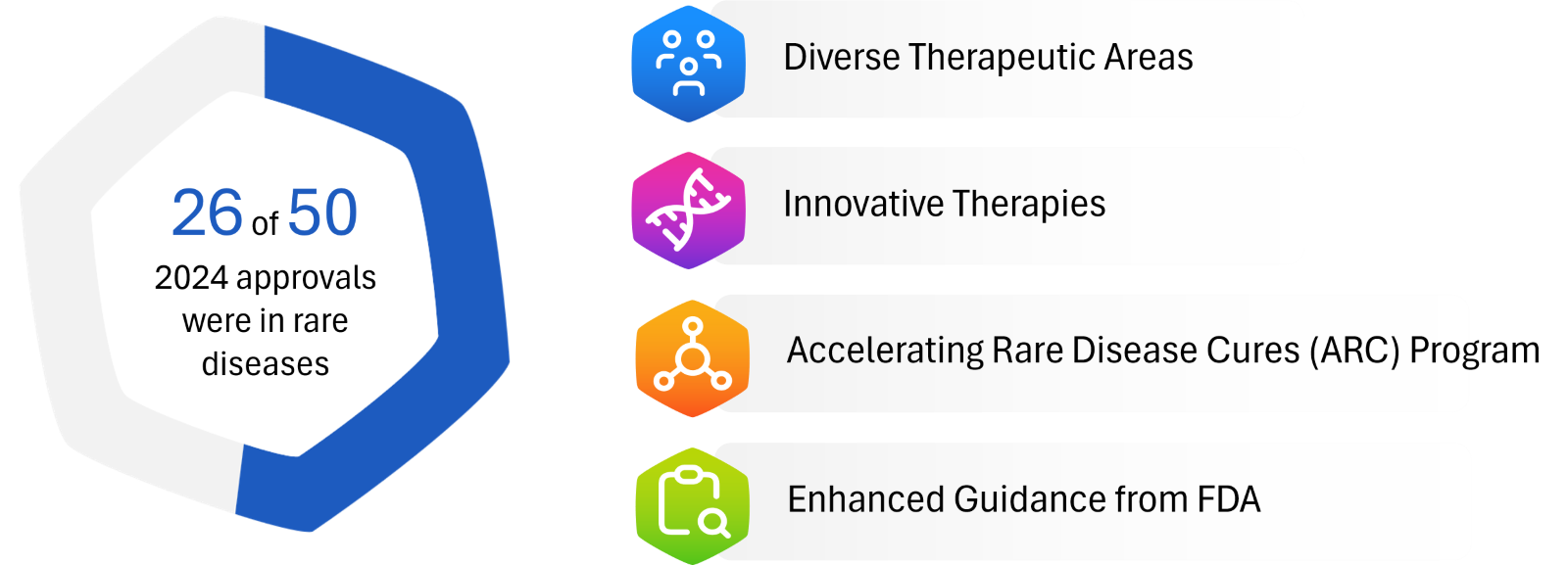
Over the past decade, drug approvals for rare diseases have risen to unprecedented levels. In 2022, 54% of the FDA’s new drug approvals targeted rare diseases, a sharp increase from 29% in 2010. These approvals span a wide range of therapeutic areas and include complex modalities such as cell and gene therapies (Figure 1). Several key factors are driving this trend. Both small biotechs and large pharmaceutical companies are showing increased commitment to rare disease pipelines, with some dedicating over 50% of their portfolios to these indications. Additionally, regulatory agencies have played a crucial role in streamlining the path to market, further accelerating the approval of these innovative therapies.
“Rare disease continues to account for a significant proportion of the global clinical development pipeline.”
Figure 1: Key Approval Trends and Regulatory Shifts in 2024
The evolving impact of regulatory guidelines
Regulatory bodies have been instrumental in shaping the landscape of rare disease drug development, providing frameworks that balance innovation with patient safety and scientific rigor while attempting to streamline and expedite the approval pathway. New guidances in the US, particularly those concerning the use of AI in medical product development, accelerated approval pathways, and the study of sex differences in clinical evaluation, have set the stage for more efficient and targeted approaches.
It is worth noting that several regulatory initiatives outside the US aim to support orphan drug development, such as the European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) Orphan Drug Regulation, which provides incentives like market exclusivity and fee reductions. Ongoing international regulatory harmonization efforts, such as those led by the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH), seek to align global orphan drug policies, streamline approval processes, and improve patient access to rare disease treatments worldwide.
The role of patient advocacy groups in regulatory policy
Alongside regulatory initiatives, patient advocacy groups have played a pivotal role in advancing rare disease drug development, ensuring that patient needs remain central to research and policy decisions. Their efforts have led to the integration of patient-reported outcomes (PROs) and patient-centric endpoints, which are now key considerations for global regulatory agencies in evaluating treatment benefits and patient quality of life. These patient-driven data points help ensure that regulatory decisions reflect the real-world impact of therapies on those living with rare diseases.
Guidance in focus: AI in rare disease drug development
The FDA’s recent guidance, Considerations for the Use of Artificial Intelligence To Support Regulatory Decision-Making for Drug and Biological Products, emphasizes the importance of transparency, reliability, and data integrity when AI-driven tools are used in submissions, analyses, or decision-making processes. It encourages sponsors to ensure that AI models are well-documented, interpretable, and validated to meet regulatory standards. AI holds significant potential in the realm of rare diseases, particularly in drug development, discovery, and clinical trial optimization, among other applications.
“Regulatory agencies do require drug developers to keep up with the evolving expectations on the use of AI tools.”
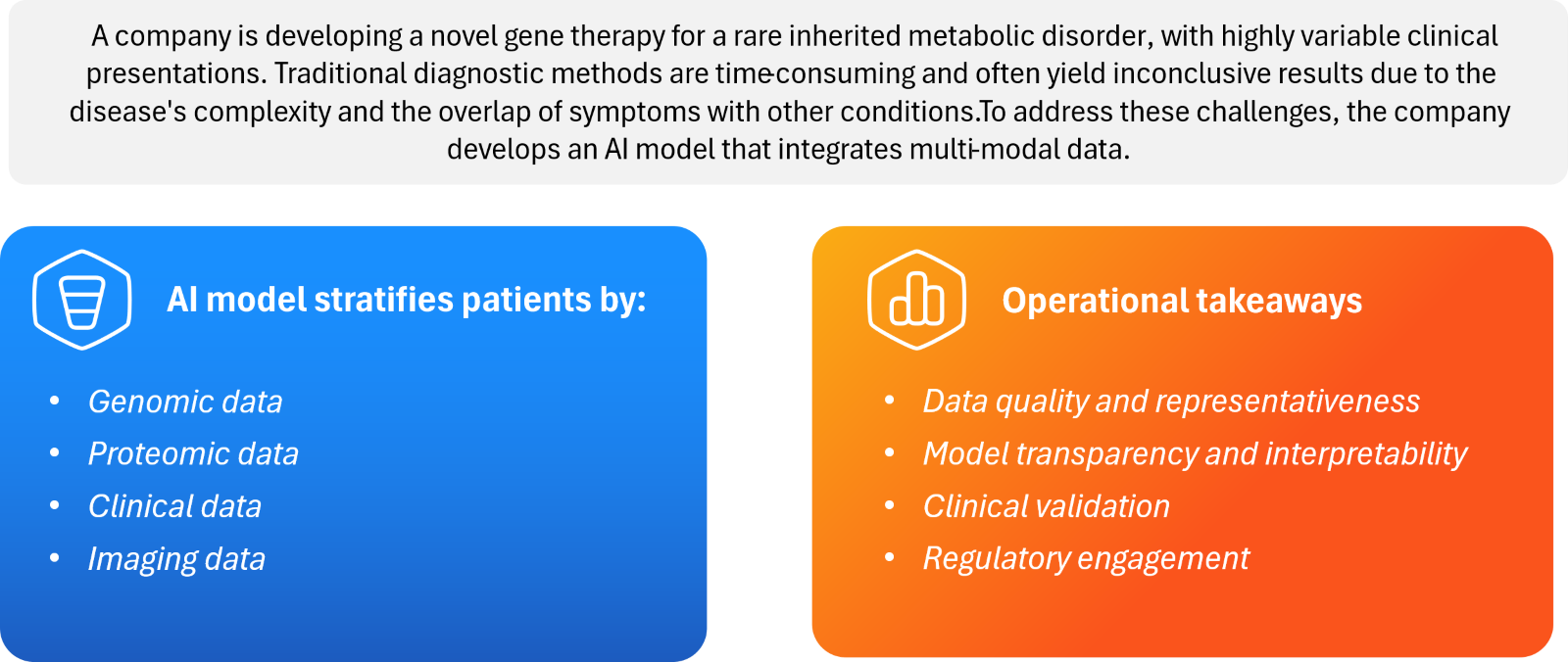
For example, by integrating genomic, proteomic, and clinical data, AI models can stratify patients more accurately (see figure 2), which is crucial given the variability in rare disease presentations. Moreover, AI can simulate trial scenarios and optimize design thereby minimizing costs and duration, which is particularly beneficial given the small patient populations involved in rare diseases.
Figure 2: Scenario: AI-Driven Diagnosis and Patient Stratification
AI models used in regulatory decision-making require continuous monitoring and updates to reflect new scientific insights and evolving data landscapes. However, by leveraging AI within the FDA’s regulatory framework, rare disease drug developers can improve efficiency, optimize clinical trials, and enhance patient outcomes while ensuring regulatory rigor and data integrity.
Guidance in focus: Accelerated approval pathways and confirmatory trials
For sponsors seeking clarity on the FDA’s expectations for utilizing the accelerated approval (AA) pathway, the guidance, Accelerated Approval and Considerations for Determining Whether a Confirmatory Trial is Underway, is a valuable resource. The AA pathway allows for the approval of drugs addressing serious or life-threatening conditions based on surrogate or intermediate clinical endpoints that are reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit.
However, to confirm long-term efficacy and safety, sponsors must conduct post-marketing confirmatory trials. The guidance outlines key factors for determining whether a confirmatory trial is “underway,” emphasizing early initiation, timely enrollment, and rigorous study design. It also stresses that confirmatory trials should begin before or shortly after receiving accelerated approval to avoid delays in verifying clinical benefit.
“You want to arrive at clear alignment with the agency as early as possible.”
By following this guidance, sponsors can streamline their development process and ensure regulatory compliance. Proactive planning and early engagement with the FDA are critical to minimizing delays and setbacks (see Figure 3).
Figure 3: Accelerated Approval and Confirmatory Trial Considerations

Guidance in focus: Sex differences in rare disease research
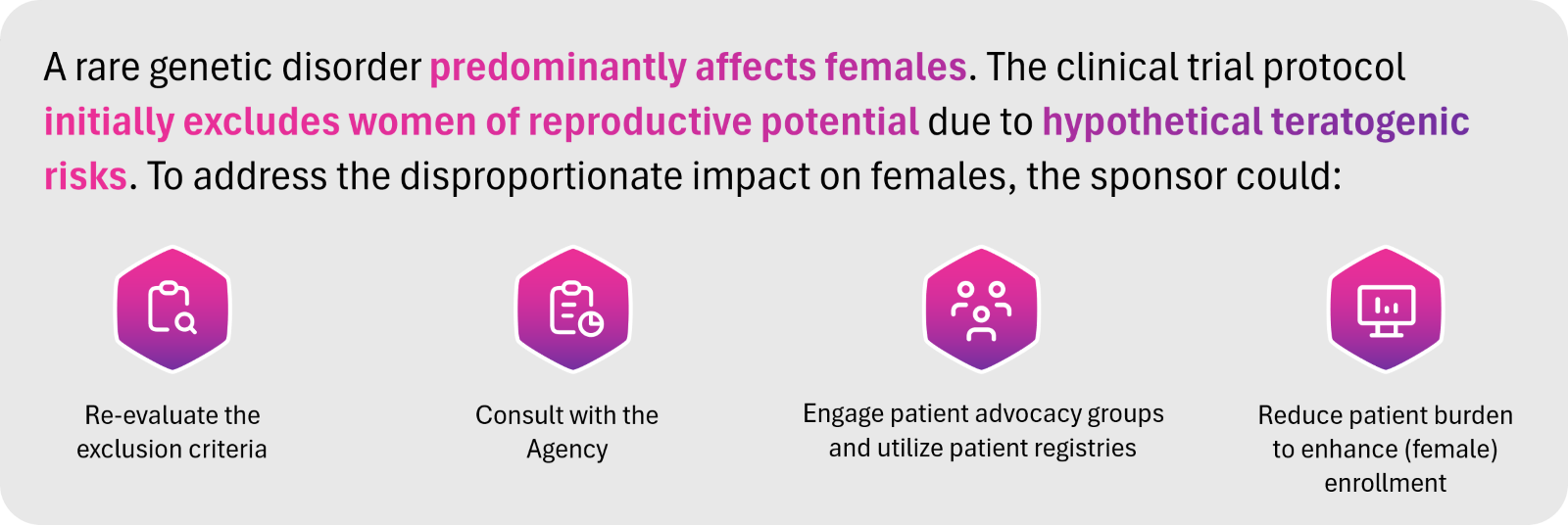
Addressing sex-based differences in medical product development, the FDA’s Study of Sex Differences in the Clinical Evaluation of Medical Products emphasizes the importance of analyzing and reporting these differences in drug safety and efficacy. The guidance highlights the need for enrolling both male and female participants in clinical trials, examining potential variations in drug metabolism, response, and adverse effects, and ensuring that sex-specific data guide regulatory decision-making. It also encourages sponsors to incorporate sex differences into preclinical and clinical study designs early in development (see Figure 4), rather than as a secondary consideration post-approval.
Figure 4: Pharmacokinetics (PK) and Pharmacodynamics (PD) Variability

For rare disease drug development, this guidance is particularly impactful. Many rare diseases disproportionately affect one sex or manifest differently between males and females, making it essential to understand these variations when developing new therapies. Given the small patient populations in rare diseases, ensuring adequate representation of both sexes when appropriate for the indication can be challenging, but failure to do so may lead to gaps in understanding treatment effects. By prioritizing early and comprehensive enrollment strategies that account for sex-based prevalence and incidence (see Figure 5), sponsors can support more equitable and scientifically rigorous development for rare diseases, leading to better outcomes for all affected populations.
Figure 5: Limited Patient Pool & Enrollment Strategies
Preparing for the future of orphan drug development
Staying informed and engaged with evolving FDA guidances is crucial for advancing rare disease drug development. These guidances reflect the agency’s commitment to adapting alongside industry needs, ultimately helping to streamline regulatory pathways and bring treatments to patients more efficiently. While regulatory interpretation can be challenging, the continued development of these frameworks provides opportunities to balance speed with quality, ensuring that innovative therapies reach those in need as quickly as possible. By proactively following and contributing to the conversation around new guidances, sponsors can optimize their development strategies, accelerate timelines, and play a vital role in shaping the future of rare disease treatment.
For support with your rare disease development program, contact us.
About Premier Research:
Premier Research, a global clinical research, product development, and consulting company, is dedicated to helping innovators transform life-changing ideas and breakthrough science into new medical treatments. We offer strategic solutions across the entire development lifecycle, from pre-clinical through commercialization, specializing in smart study design and full-service clinical trial management.
Leveraging technology and therapeutic expertise, we deliver clean, conclusive data with a focus on reducing development timelines, securing access to the right patients, and effectively navigating global regulations to ensure submission-ready results.
As an organization that puts patients first, we pride ourselves on helping customers answer the unmet needs of patients across a broad range of medical conditions. Visit premier-research.com.
[i]: https://www.rarediseaseday.org/what-is-a-rare-disease/

 Webinar
Webinar 


 Perspectives Blog
Perspectives Blog