Pharmacovigilance is a critical pathway to successful drug development. This pathway helps identify the risks of a product and understand the safety profile, thereby allowing sponsors to balance risks with the benefits while safeguarding patients. Outsourcing this part of the development process comes with its own benefits and risks. This blog explores the essential components of managing and optimizing drug safety through outsourced services while establishing effective oversight of safety vendors.
A brief introduction to clinical safety
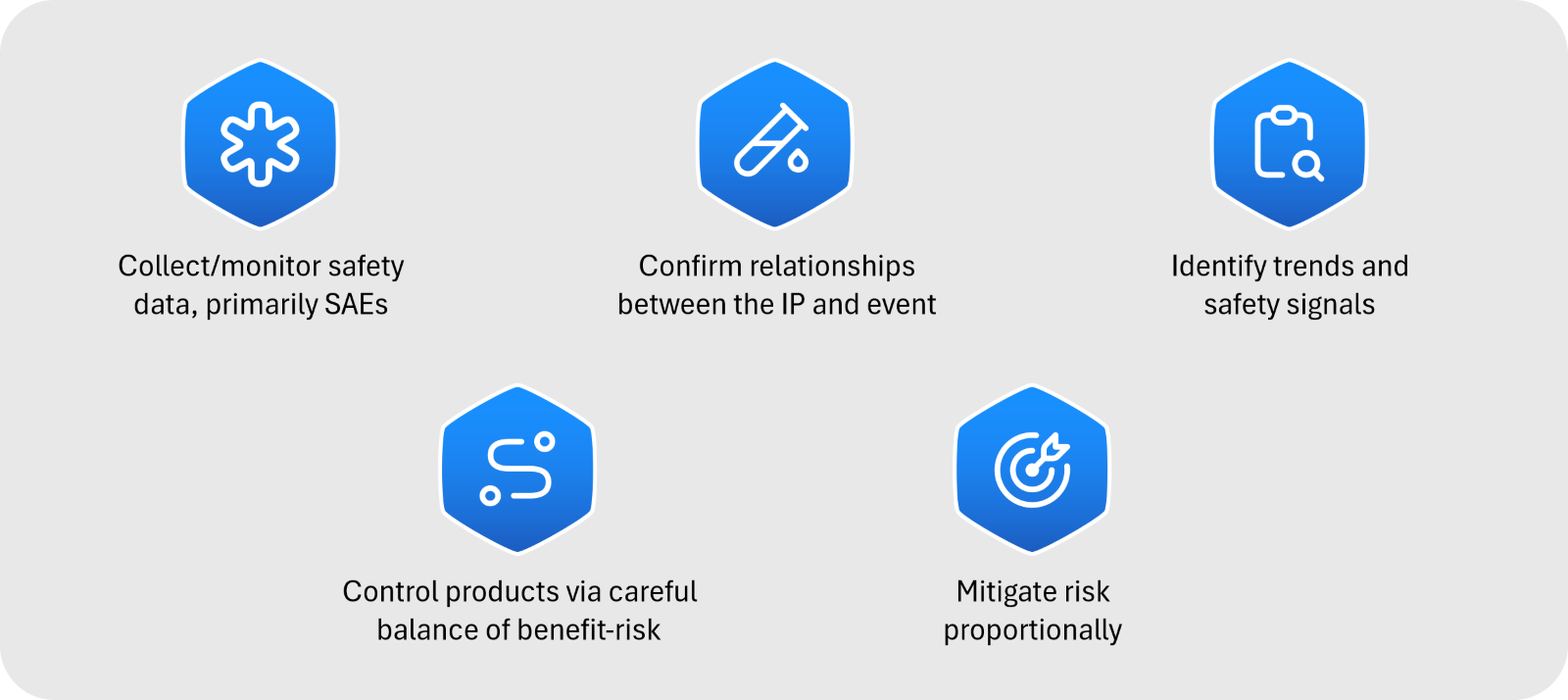
Pharmacovigilance plays a crucial role in managing the risks and benefits of drugs throughout their lifecycle. This process involves identifying adverse reactions and mitigating them while ensuring the drug’s efficacy remains beneficial for the patient population (see Figure 1).
“The sole purpose of pharmacovigilance can be reduced down to identifying adverse reactions and mitigating against them to optimize patient safety.”
In clinical trials, where the environment is highly controlled, the goal is to monitor both anticipated and unknown risks. Anticipated risks might emerge from earlier research phases such as pre-clinical in vitro, in vivo or in-silo studies, while some risks may only become apparent during trials.
Managing safety concerns
The balance between risk and benefit varies depending on the indication and patient population. For instance, in oncology, there may be a higher tolerance for adverse reactions as justified by the potential life-saving benefits in patients where the prognosis is poor.
Where safety concerns are identified, several factors should be considered when managing risks, including:
- Patient selection: Control the patient population by excluding those with pre-existing conditions or specific age groups.
- Dosage regulation: Optimize dosage to achieve the highest efficacy with the lowest risk.
- Administration methods: Adapt the formulation or administration route to minimize adverse effects.
- Early attrition: Identifying potential risks early can safeguard patients and conserve valuable resources that can be diverted to more promising development candidates.
Figure 1: Introduction to clinical safety/pharmacovigilance
Optimizing outsourced services: Safety databases
“When it comes to clinical safety, proportionally leveraging technology against volume is crucial.”
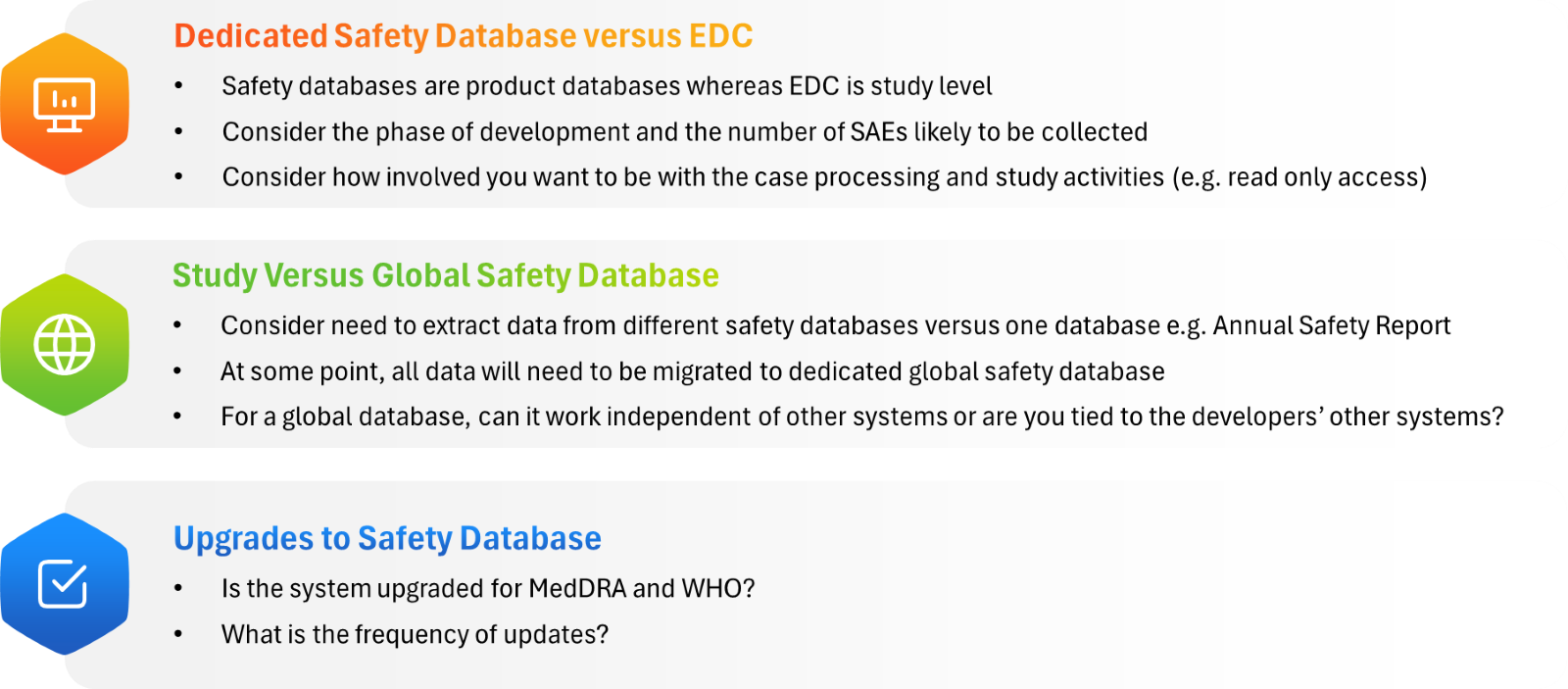
Outsourcing safety databases in clinical trials involves several considerations to ensure the most cost effective and compliant solution for the specific trial and product (see Figure 2). While small trials might use the study Electronic Data Capture (EDC) system, larger trials and programs may necessitate a dedicated safety database.
Figure 2: Key considerations for safety databases
Additional factors to keep in mind include:
- Access and control: Sponsors must ensure they have appropriate access to safety data. Consider direct access to the safety database versus outputs provided by the vendor to allow for real-time oversight and flexibility in reporting.
- Integration:
- Evaluate the cost and feasibility of integrating the EDC with safety databases versus volume of data. Integration ensures seamless data exchange and avoids duplication errors, but the costs must be proportionate to the volume of data being handled.
- Compatibility with signal detection tools and pharmacovigilance analytics should also be assessed.
- Data security and compliance: Ensure that the database meets GDPR, HIPAA, and FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance standards. Data encryption, role-based access, and audit trails are crucial for protecting patient safety data.
- Scalability: As trials progress into later phases, the volume of safety data grows exponentially. Selecting a database that scales with study needs prevents costly migrations and disruptions.
Effective SAE reporting from sites: Methods and considerations
Serious Adverse Event (SAE) reporting is a critical component of clinical trials. Efficient reporting requires clear communication between sites and the pharmacovigilance team. There are various methods to streamline this process, from electronic forms to integrated systems.
“There are three main ways to get SAEs in: Electronic forms, end-to-end integration between the safety database and EDC, and EDC notifications to the PV team.”
To enhance SAE reporting, key factors to assess include:
- Electronic SAE forms:
- Consider SAE forms via email for low data volumes
- Simplify data collection by configuring forms within the EDC system for direct extraction, reducing manual entry burden on sites and ensuring timely reporting.
- Ensure the form is fit for purpose.
- Forms that are set-up poorly can result in more work for the PV teams and the sites.
- Integration solutions: Consider cost-effective integration strategies for high-volume data to avoid duplicate entry and improve consistency. Ensuring compatibility with safety databases, pharmacovigilance platforms, and regulatory submission portals is essential.
- Automated alerts and AI-driven processing: Implement automated proportionate SAE alerts that notify pharmacovigilance teams in real time. AI-powered tools can assist in preliminary case assessment, reducing the burden on clinical teams and expediting critical decision-making.
- Real-time monitoring and dashboards: Leverage centralized safety dashboards to track SAE trends, ensuring rapid response to potential safety signals and regulatory inquiries.
- Compliance and data security: Ensure that SAE reporting aligns with ICH E2B(R3), FDA, and EMA reporting standards, maintaining audit trails and robust data security protocols.
Vendor oversight and safety monitoring
Effective vendor oversight is essential when outsourcing clinical safety to ensure data integrity, regulatory compliance, and patient protection. While outsourcing can enhance efficiency and expertise, sponsors remain ultimately responsible for pharmacovigilance activities. Strong oversight helps mitigate risks by ensuring vendors adhere to safety protocols, maintain high-quality reporting standards, and comply with global regulations (see Figure 3).
“Oversight is about ensuring accountability without stifling the innovation and efficiency that outsourcing can offer.”
Figure 3: Key components of vendor oversight

Implementing oversight mechanisms
- Do your due diligence: Before selecting a vendor, explore the vendors inspection history. For example, have they had any critical findings?
- KPIs and performance levels: Define and monitor quantifiable KPIs to assess compliance with regulatory standards and contractual obligations. Establish predefined corrective actions for any breaches to mitigate risks proactively.
- Governance structures: Establish clear escalation paths, governance charters, and regular vendor audits to ensure effective safety data management and adherence to compliance expectations.
- Inspection histories and due diligence: Evaluate the vendor’s inspection history, regulatory track record, and data integrity controls during the RFP process. Prioritize vendors with a strong history of compliance with regulatory authorities such as FDA, EMA, and MHRA.
- Risk-based auditing and continuous monitoring: Implement routine audits and real-time monitoring systems to detect early warning signs of non-compliance. Risk-based vendor assessments can help focus resources on high-impact areas.
- Technology-enabled oversight: Leverage automated dashboards and real-time reporting tools to track vendor performance metrics efficiently. Digital risk mitigation platforms can enhance transparency and decision-making.
- Communication and issue resolution: Maintain open communication channels through regular governance meetings, issue resolution frameworks, and CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) plans to address concerns in a timely manner.
Safeguarding your most sensitive clinical trial data
Navigating the complexities of pharmacovigilance in clinical trials requires a strategic approach to managing drug safety, optimizing databases, and maintaining effective oversight. By balancing risks and benefits, leveraging technology, and fostering transparent partnerships, sponsors can ensure the safety and efficacy of their clinical programs. Understanding the dynamics of pharmacovigilance and implementing effective safety strategies can significantly enhance the outcomes of clinical trials, ultimately leading to safer and more effective treatments for patients.
For support with your clinical safety needs, contact us.
ABOUT PREMIER RESEARCH:
Premier Research, a global clinical research, product development, and consulting company, is dedicated to helping innovators transform life-changing ideas and breakthrough science into new medical treatments. We offer strategic solutions across the entire development lifecycle, from pre-clinical through commercialization, specializing in smart study design and full-service clinical trial management.
Leveraging technology and therapeutic expertise, we deliver clean, conclusive data with a focus on reducing development timelines, securing access to the right patients, and effectively navigating global regulations to ensure submission-ready results.
As an organization that puts patients first, we pride ourselves on helping customers answer the unmet needs of patients across a broad range of medical conditions. Visit premier-research.com.